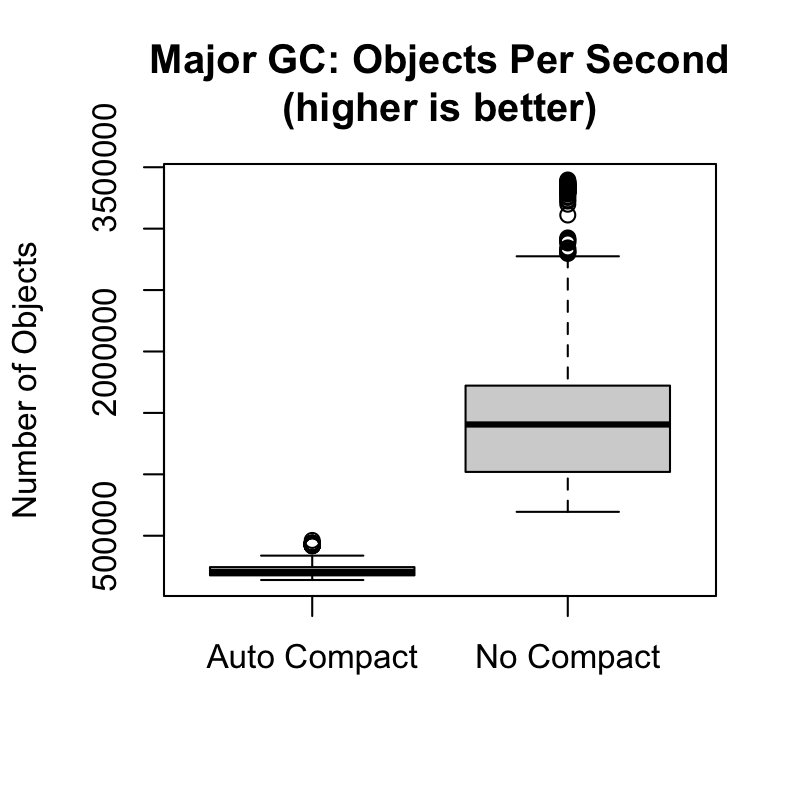
Feature #17176
closedGC.auto_compact / GC.auto_compact=(flag)
Description
Hi,
I'd like to make compaction automatic eventually. As a first step, I would like to introduce two functions:
- GC.enable_autocompact
- GC.disable_autocompact
One function enables auto compaction, the other one disables it. Automatic compaction is disabled by default. When it is enabled it will happen only on every major GC.
I've made a pull request here: https://github.com/ruby/ruby/pull/3547
This patch makes object movement happen at the same time as page sweep. When one page finishes sweeping, that page is filled.
Sweep + Move Phase¶
During sweep, we keep a pointer to the current sweeping page. This pointer is kept in heap->sweeping_page. At the beginning of sweep, this is the first element of the heap's linked list.
At the same time, the compaction process points at the last page in the heap, and that is stored in heap->compact_cursor here.
Incremental sweeping sweeps one page at a time in the gc_page_sweep function. At the end of that function, we call gc_fill_swept_page. gc_fill_swept_page fills the page that was just swept and moves the movement cursor towards the sweeping cursor.
When the sweeping cursor and the movement cursor meet, sweeping is paused, and references are updated. This can happen in 2 ways, the sweeping cursor "runs in to the moving cursor" which is here. Or the moving cursor runs in to the sweep cursor which happens here.
Either way, the sweep step is paused and references are updated.
Reference Updating¶
Reference updating hasn't changed, but since reference updating happens before the GC finishes a cycle, it must take in to account garbage objects here.
Read Barrier¶
During the sweep phase, some objects may touch other objects. For example, T_CLASS must remove itself from a parent class.
class A; end
class B < A; end
const_set(:B, nil)
When B is freed, it must remove itself from A's subclasses. But what if A moved? To fix this, I've introduced a read barrier. The read barrier protects heap_page_body using mprotect. If something tries to read from the page, an exception will occur and we can move all objects back to the page (invalidate the movement).
The lock function is here.
The unlock function is here.
It uses sigaction to catch the exception here.
Cross Platform¶
mprotect and sigaction are not cross platform, they doesn't work on Windows. On Windows the read barrier uses exception handlers that are built in to Windows. I implemented them here.
The read barrier seems to work on all platforms we're testing.
Statistics¶
GC.stat(:compact_count) contains the number of times compaction has happened, so we can write things like this:
GC.enable_autocompact
cc = GC.stat(:compact_count)
list = []
loop do
500.times { list << Object.new }
break if cc < GC.stat(:compact_count)
end
p GC.stat(:compact_count)
We can check when the read barrier is triggered with GC.stat(:read_barrier_faults)
I've also added GC.latest_compact_info so you can see what types of objects moved and how many. For example:
[aaron@tc-lan-adapter ~/g/ruby (autocompact)]$ cat test.rb
list = []
500.times {
list << Object.new
Object.new
Object.new
}
GC.enable_autocompact
count = GC.stat :compact_count
loop do
list << Object.new
break if GC.stat(:compact_count) > count
end
p GC.latest_compact_info
[aaron@tc-lan-adapter ~/g/ruby (autocompact)]$ make runruby
./miniruby -I./lib -I. -I.ext/common ./tool/runruby.rb --extout=.ext -- --disable-gems ./test.rb
{:considered=>{:T_OBJECT=>408}, :moved=>{:T_OBJECT=>408}}
[aaron@tc-lan-adapter ~/g/ruby (autocompact)]$
Recap¶
New methods:
- GC.enable_autocompact
- GC.disable_autocompact
- GC.last_compact_info
New statistics in GC.stat:
- GC.stat(:read_barrier_faults)
Diff is here: https://github.com/ruby/ruby/pull/3547